This study, published in Nature Communications (2025) by Pritam Saha et al., explores how tiny changes (mutations) in the tip-link protein—essential for hearing—can lead to hearing loss. It reveals how prolonged force from loud sound affects the protein’s structure and function, highlighting key molecular interactions that influence its stability and behavior. By comparing normal and mutant proteins, the research sheds light on how hearing-related proteins have evolved to handle mechanical stress.
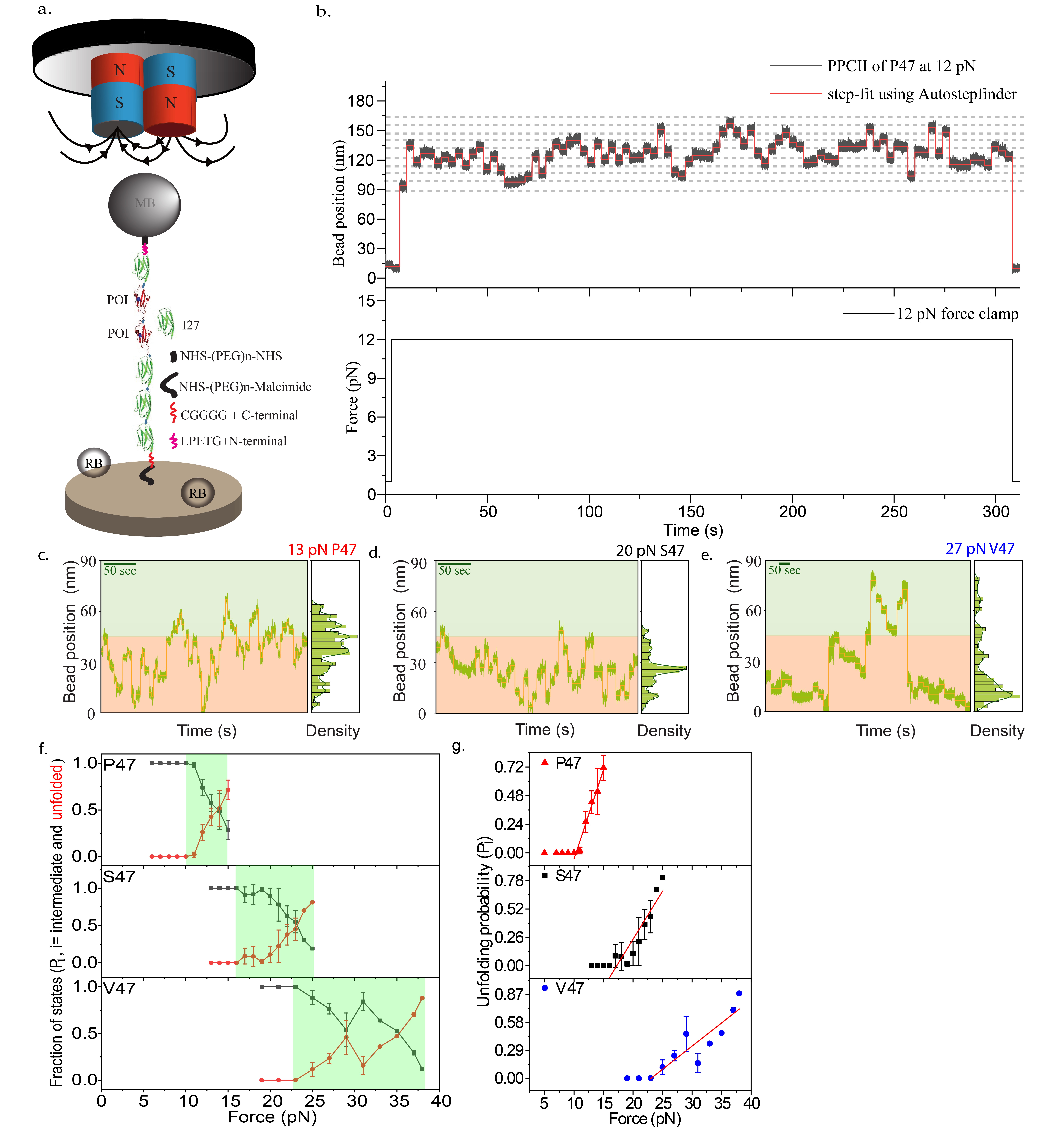
Figure: (a). Design of a Lab-built Magnetic Tweezer with single-biomolecule tether, (b). example of 5 minutes long force-clamp data with microstates, and (c,d,e,f) varying mechano-stability of wild-type variants and mutant, showing stochasticity in folding dynamics and (g) and quantitative estimation of cooperativity of the protein variants.

